Technology
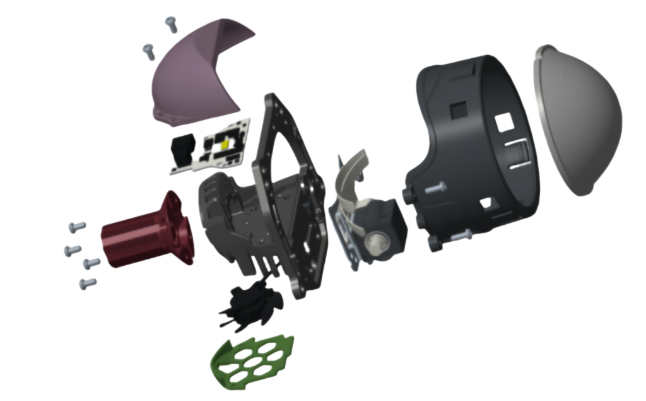
Lens Technology
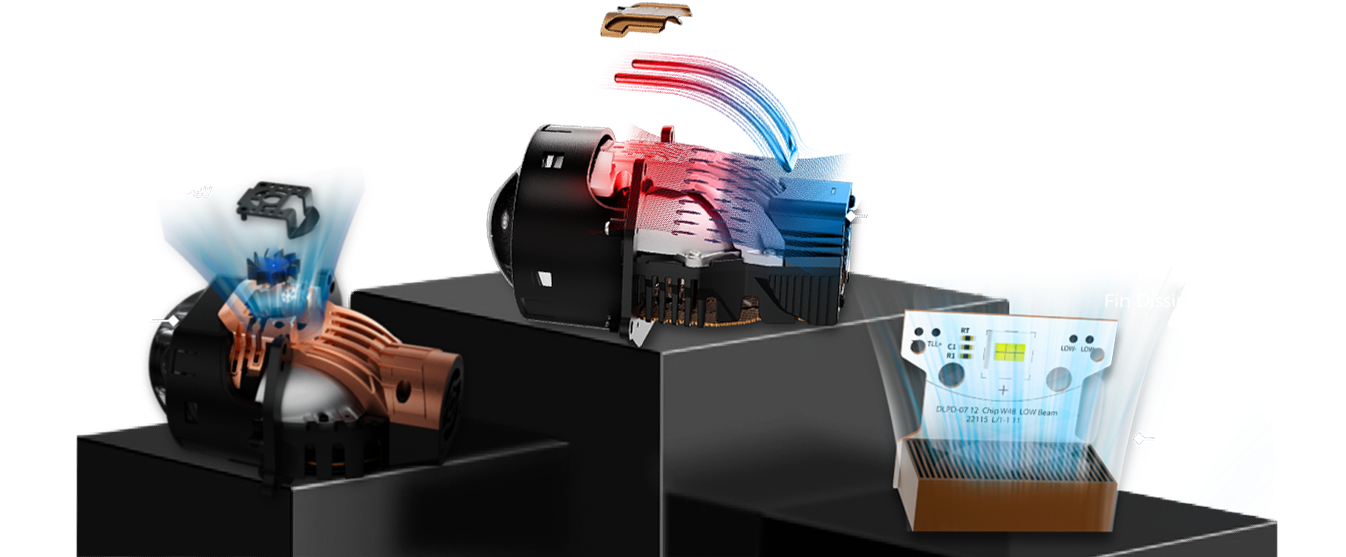

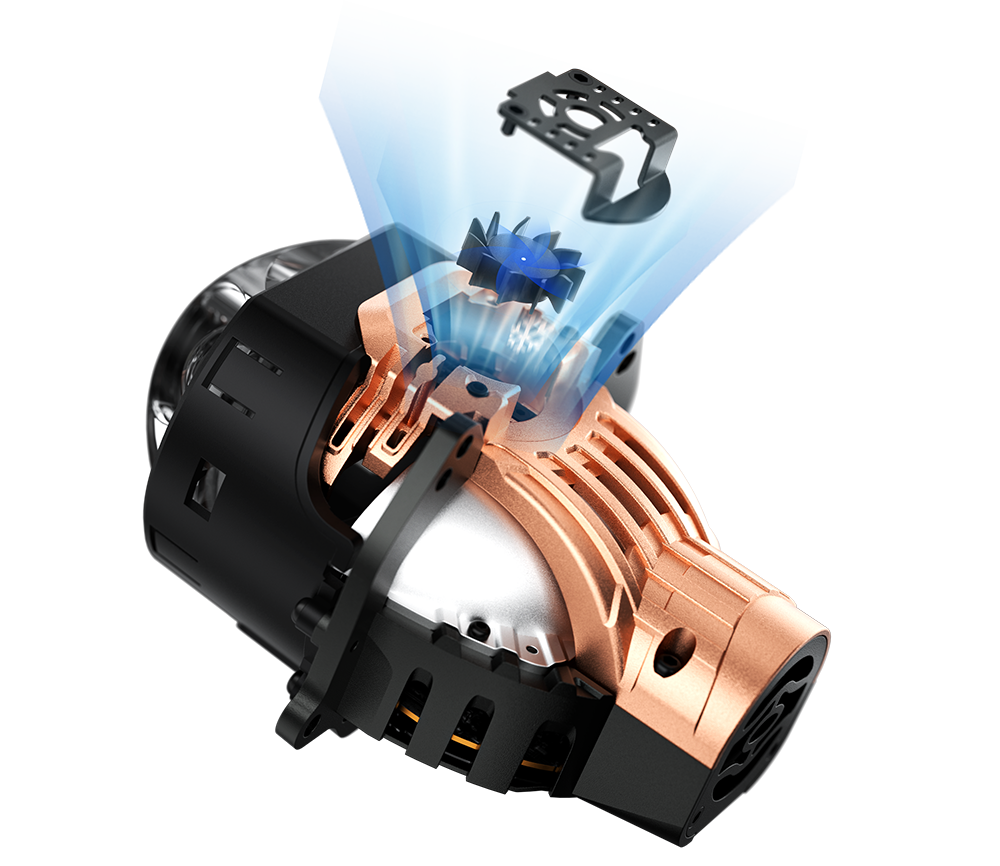
Heat Pipe Technology
Heat pipes are passive heat transfer elements with very high thermal conductivity.
The walls of the heat pipe are equipped with a suction core.
The capillary force generated by the wick returns the condensate from the condensing end to the evaporating end.

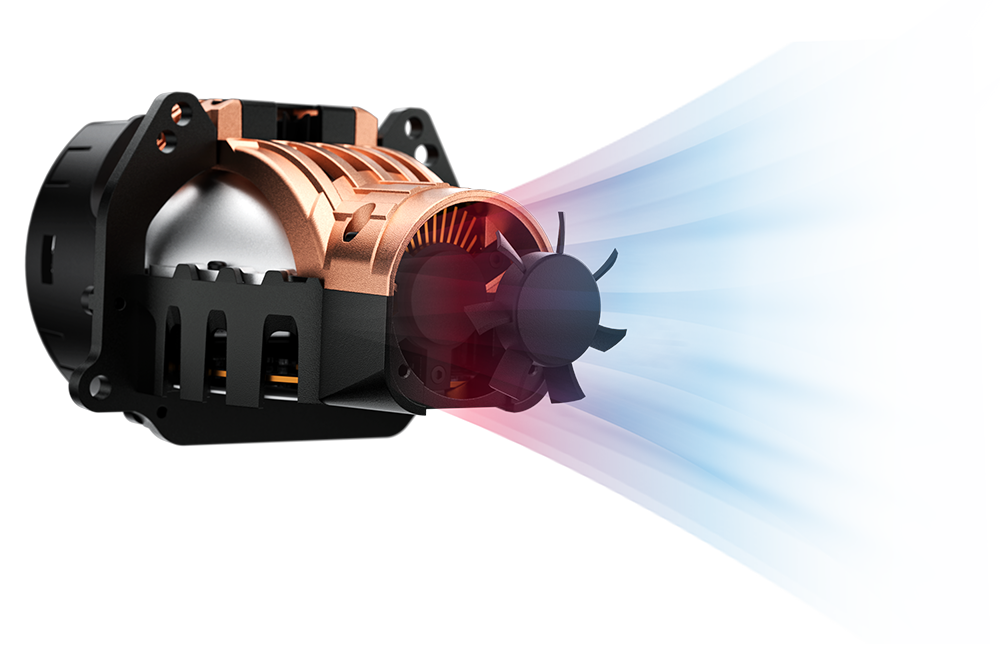
Silent Fan Convection Cooling
Thermal convection is a type of heat dissipation in which heat is exchanged through the flow of gases. The greater the wind speed, the more heat is dissipated.
ultra high speed


Fins
Heat Dissipation
The fin cooling principle is the principle of utilizing the shape and arrangement of fins to increase the heat dissipation area and improve the heat dissipation efficiency. The multiple teeth of the fins increase the heat dissipation area, making it easier for the heat to be emitted into the air, thus effectively improving the heat dissipation efficiency.


centrifuge
Fan Cooling Technology
1. Centrifugal fan is mounted to the top of the front of the direct radiator and extractor fan is mounted to the bottom of the front of the direct radiator; 2. The direct radiator is fitted with a heat pipe running from top to bottom so that the heat source of the direct light bead at the top is diverted to the bottom; 3. Install heat sink fins on the low beam plate near the bottom of the direct radiator to increase the heat dissipation area.
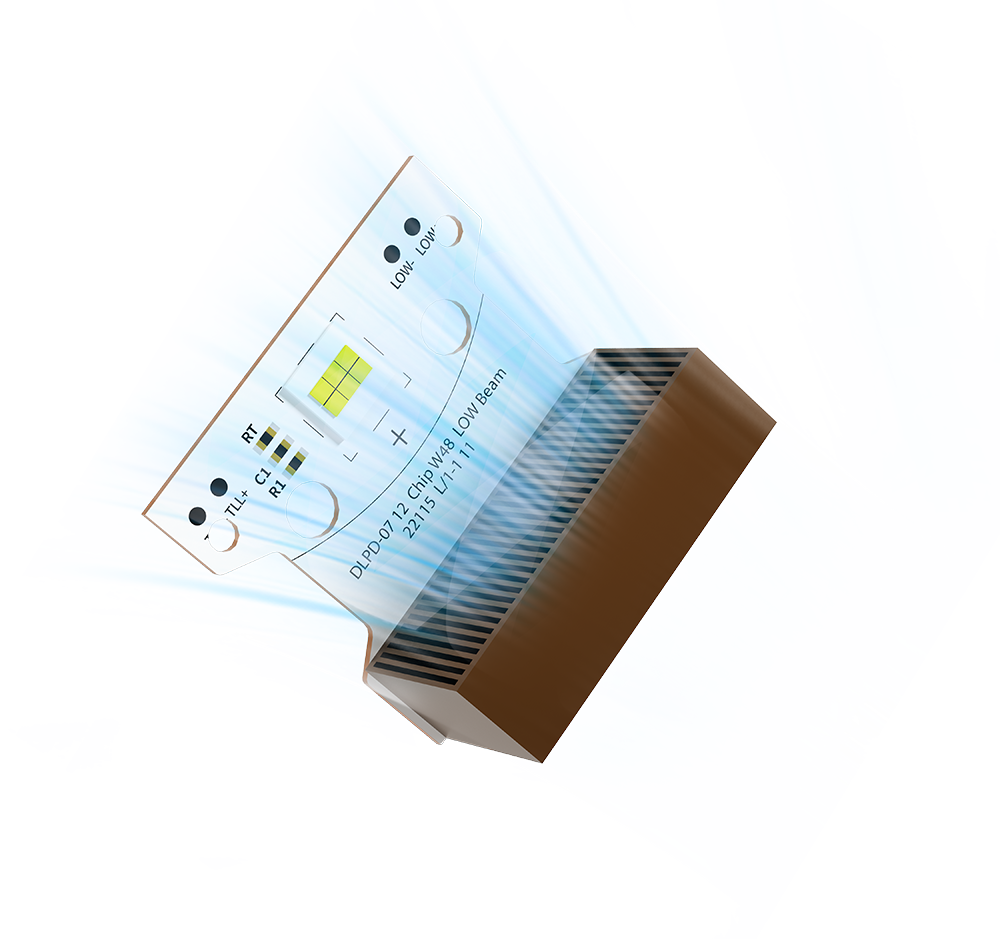
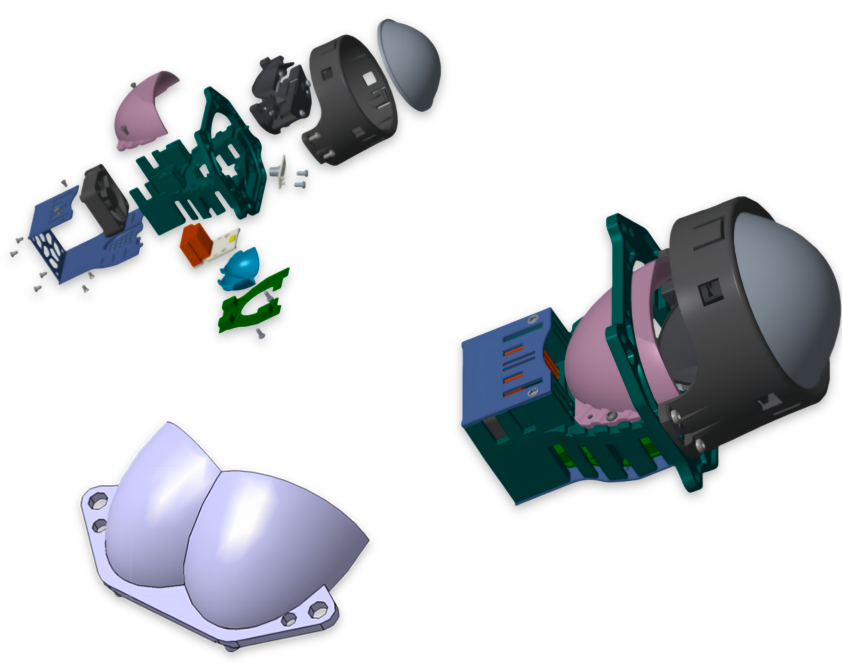
optical
Single Reflector Bi LED Lens
01
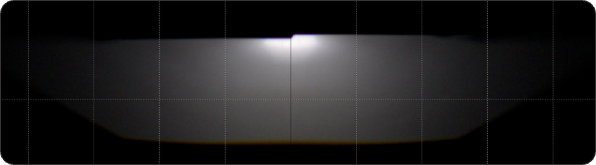
Low Beam
Uniform low beam pattern, left and right widths greater than 40 degrees, bright spot in the center, sharp tangent lines.

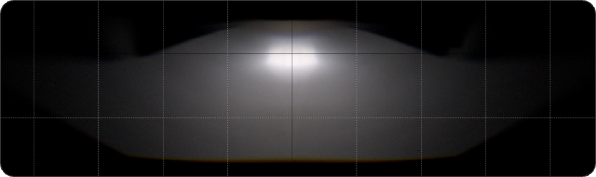
High Beam
High beam is semi-circular, wide irradiation range, the center of the bright spot is obvious, good paving effect.
02
optical
Double-Reflector Bi LED Lens
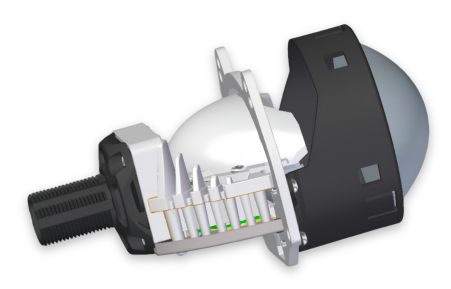
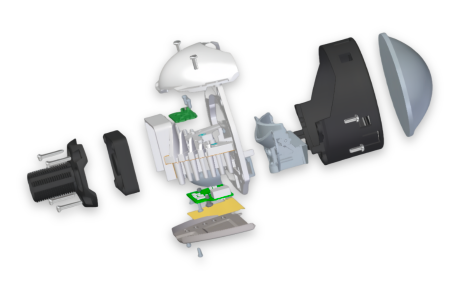
Low Beam
Uniform low beam pattern, left and right width greater than 40 degrees, bright spot in the center, sharp tangents.

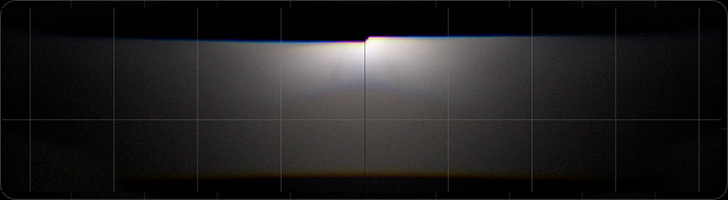
High Beam
High brightness in the center of the high beam pattern, obvious fill-in light spot, far irradiation distance, good paving effect.
optical
M Reflector Bi LED Lens
03
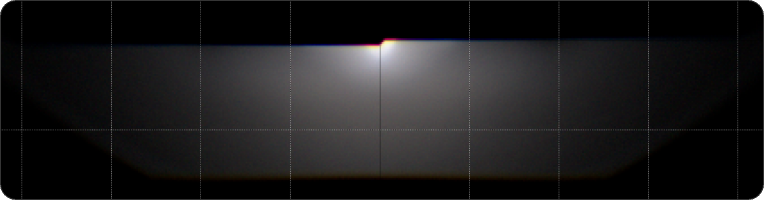
Low Beam
Low beam type left and right width is more than 40 degrees, uniform brightness, sharp cut line.

High Beam
The high beam is HELLA light type, the height is suitable, the width of both sides is more than 40 degrees, the complementary light spot is obvious, strong penetrating force.
04
optical
Double-Reflector Bi LED Lens
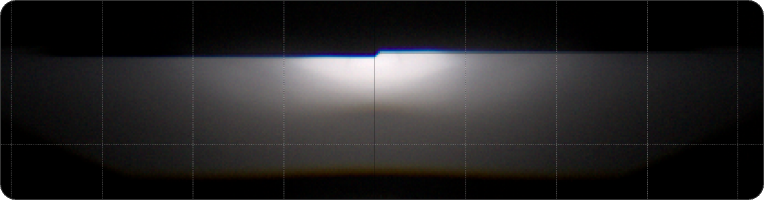
Low Beam
Low beam type left and right width is more than 40 degrees, uniform brightness, sharp cut line.

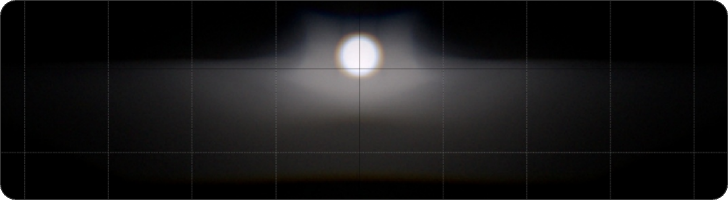
High Beam
The high beam is HELLA light type, the height is suitable, the width of both sides is more than 40 degrees, the complementary light spot is obvious, strong penetrating force.
optical
Single Reflector Bi LED Lens
05

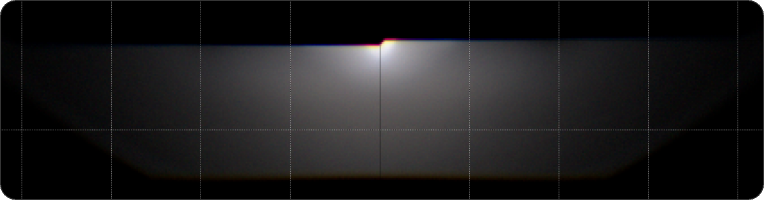
Low Beam
Square glass, no light blocking in the lower part of the low beam type, good uniformity, bright spot in the center, good road illumination effect.

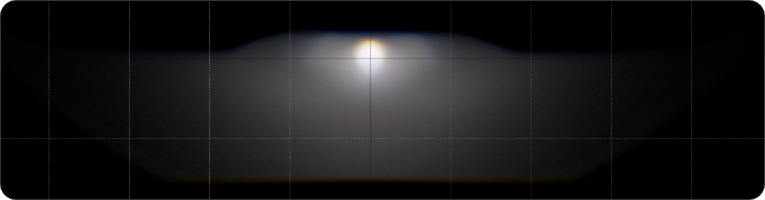
High Beam
The center of high beam type is a small direct sun spot, high brightness in the center, surrounded by a halo, small gradient of brightness and darkness change, good penetrability
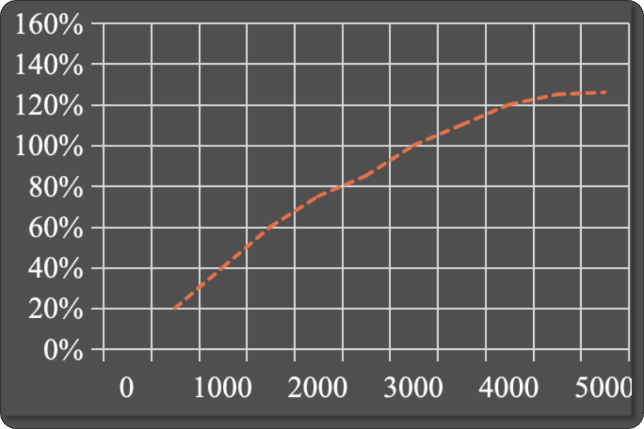
Luminous Flux vs. Forward Current
The size of the luminous flux is not only related to the current of the lamp bead, but also related to the luminous efficiency of the lamp bead. As can be seen from the figure, when the lamp bead current exceeds 80% of the maximum current, with the increase in current, the luminous flux increases very little, most of the power is converted into lamp bead heat. Therefore, the higher the driving efficiency of LED headlights, the choice of LED lamp bead luminous efficiency is higher, the larger the lamp bead crystal, the larger the luminous flux, and the input power is not directly related to the input power is not the larger the brighter!